In the last 20 years, the number of adults diagnosed with diabetes has more than doubled, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; but a D.C. doctor who treats the disease is encouraged by recent advances in therapies.
Diabetes occurs when blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. The most common form of diabetes in the D.C., Maryland and Virginia area is Type 2 diabetes.

“In Type 2 diabetes, the greatest risk to one’s health is having cardiovascular disease, having a heart attack, having a stroke, just dying of cardiovascular complications,” said Dr. Mansur Shomali, of MedStar Health.
But, Shomali said doctors now know that lowering the glucose level isn’t enough. How glucose is lowered is important, and the newest treatments address that.
“There are modern medications that we use that actually reduce the risk of those (cardiovascular) complications, which we didn’t have a few years ago. So, this is really an exciting time for diabetes specialists like myself, and people living with diabetes,” he said.
November is National Diabetes Month.
Shomali specializes in endocrinology, diabetes and metabolism. He said lots of myths come with diabetes.
“I feel like the greatest myth is that they did something wrong, that they ate too many carbs,” he said. “But diabetes isn’t caused by one thing that someone does; it’s really complicated.”
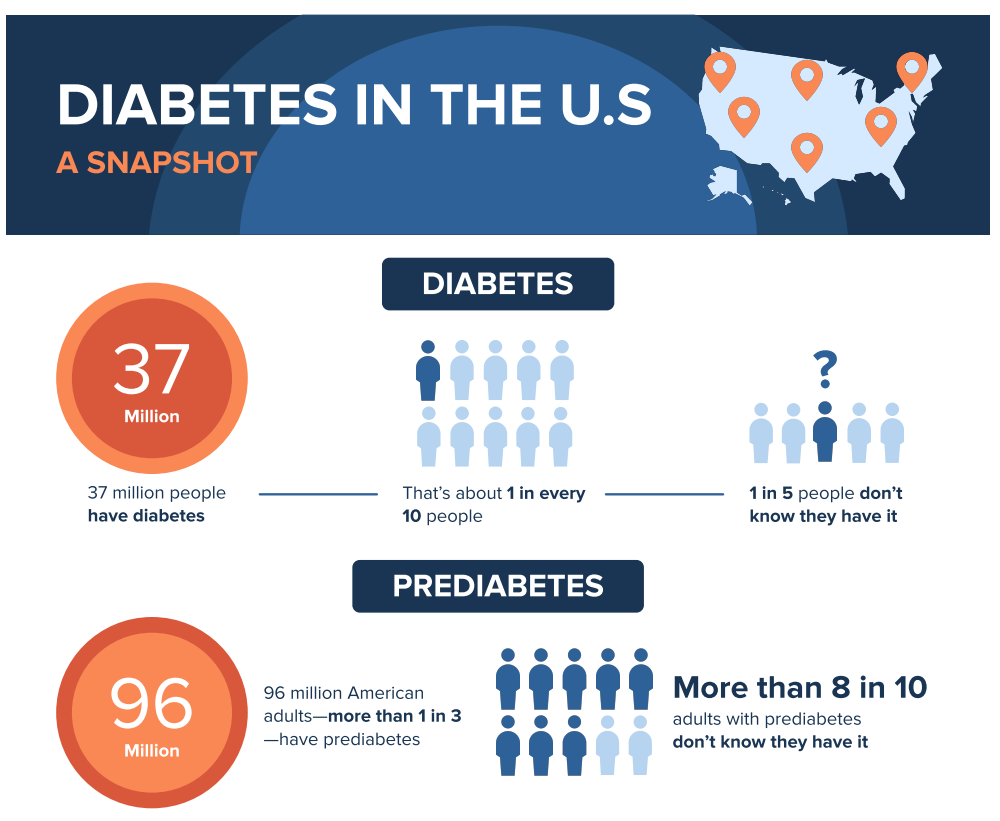
About one in 10 people, 36 million Americans, live with diabetes. There is no cure. But losing weight, eating healthy food and being active can help. Even sleep can have an impact.
“If we don’t sleep well, we increase our risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease,” he said.
People who have Type 2 diabetes, in particular, are also at a much higher risk for certain cancers than people without diabetes.
“But those risks can be reduced and mitigated with appropriate treatment. So the treatments aren’t just about lowering the blood sugar, they are about addressing all the factors that I said before — diet, exercise activities, sleep, taking the right medications for diabetes — as opposed to some of the older medications that don’t work as well,” he said.
One in five people with diabetes doesn’t know it, according to the CDC. Shomali recommends that people get screened and receive appropriate help.
“Seeing someone who’s well-versed in those new therapies and knows how to prescribe them,” he said.
MedStar Health surveyed 656 people in D.C. in October, asking them about Type 2 diabetes. Their answers revealed the misconceptions and myths surrounding diabetes, including:
- Eating too much sugar causes diabetes. (55%)
- If someone is on insulin, it means they aren’t doing a good job of managing their blood sugar. (40%)
- Diabetes runs in families, so only people with a diabetic family member have to worry about getting the disease. (30%)
- People who have diabetes can never eat sweets. (27%)
- You can stop taking diabetes medicine once your blood sugar is under control. (26%)
- Diabetes is inconvenient but not serious. (20%)
- There’s nothing you can do to prevent diabetes. (19%)
You can learn about programs proven to prevent or delay Type 2 diabetes on the CDC website.