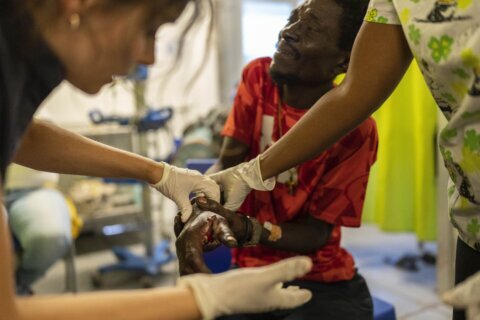
Compassion is an important concept in medicine. This is why it is frequently discussed in medical school applications. However, compassion often is used as a buzzword without sufficient attention to what it really means and why it is so important.
For aspiring physicians, it is worthwhile to understand what compassion means and its role in providing medical care. By taking time to think about the concept in more depth, med school applicants can write about compassion more effectively in their applications and discuss it in a more sophisticated fashion in their medical school interviews.
What Is Compassion in Medicine?
When we ask students to define compassion, we often get varied responses. Even health care providers who may have a strong grasp of the concept sometimes have difficulty expressing it in a tangible way.
[READ: 6 Signs of a Compassionate Medical School.]
A study published in the International Journal of Palliative Nursing in 2016 sought to define compassion in the context of health care by reviewing previous literature written on the topic. Not surprisingly, the investigators found that in medical literature, compassion was defined in different ways by different authors.
However, some common themes emerged from the study. Its authors examined the themes and distilled compassion into several elements. One is the ability to show sensitivity or to understand another person’s pain. In this way, they argued, compassion is similar to empathy.
However, according to the authors, there is another element to compassion that goes beyond empathy — the desire to go out of one’s way to help a suffering person. Other experts have argued that in the context of health care, compassion also involves effectively communicating with patients.
[Read: Cultivate Communication Skills for Med School Admissions Success.]
Compassion needs to be distinguished from pity because compassion is a positive attribute that comes from generosity and a desire to connect with others. Pity, on the other hand, is considered a negative emotion. One who is compassionate toward another person sees the other person as equal. By contrast, someone who feels pity for another person views the other person with condescension.
Why Is Compassion Important in Medicine?
This may seem like an obvious question. After all, most of us want to feel cared for when we experience difficulty. It is comforting to know that when we are going through an illness, our care providers can relate to us, put themselves in our shoes and do everything in their power to help us.
But beyond these self-evident reasons, there is another argument for why compassion matters. It turns out that providing compassionate medical care may lead to better patient outcomes.
Some experts argue that compassion leads patients to adhere more to medical treatments. A patient with high blood pressure, for example, may be more inclined to take his blood pressure medication regularly if he feels that his physician is compassionate.
Studies have shown that patients with diabetes whose physicians were more empathetic tended to achieve better blood sugar and blood cholesterol levels. Other examples abound in medical literature showing that compassion can improve patient care, and premed students are encouraged to go beyond this article to explore the topic.
How Can Compassion Be Acquired?
A common misconception is that compassion cannot be learned, that it is something a person either possesses or does not. However, research in this area suggests otherwise. Studies have shown that empathy, a component of compassion, can be increased through training. There is also biological evidence that training people to be compassionate may lead to positive changes in neural network activity in the brain.
[Read: 5 Key Characteristics of Successful Medical School Applicants.]
Different approaches have been proposed for increasing compassion. For example, some research demonstrates a role for mindfulness meditation programs. When a group of college students were randomly assigned to either three weeks of a self-guided mindfulness meditation regimen or to a program that improved cognitive skills, those in the mindfulness meditation group displayed greater compassion toward others after the program.
To increase compassion, students should take part in service-based activities. This idea is also backed by research. For example, in a study of nursing students published in Nurse Education in Practice in 2018, participation in an activity to provide service to populations experiencing homelessness resulted in greater levels of empathy and improved attitudes toward the challenges that homeless people face.
By getting involved in community service projects where you can help those in need or working at a clinic where you can assist underserved populations with medical care, you will learn about the challenges that others face, develop greater sensitivity and become more motivated to serve. In doing so, you can show medical school admissions committees that you are striving to increase your level of compassion, in turn making you a better candidate for med school.
When writing about compassion in medical school applications as an aspiring physician, strive to explain what compassion means to you and draw on examples where you have seen compassion at play. Most importantly, view compassion as a skill that you can build on over the course of your training and your future career so that you can constantly improve the quality of care you provide to patients.
More from U.S. News
Ways Medical School Applicants Send the Wrong Signal
10 Actions That Hurt Your Medical School Chances
Common Mistakes Premeds Make When Reflecting on Community Service
Why Medical School Applicants Should Highlight Compassion originally appeared on usnews.com